ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Disruption - VUCA
Volatility: speed of change in an industry, market, or overall environment
Uncertainty: lack of predictability in an environment
Complexity: number of issues and amount of confusion that surround the organization
Ambiguity: lack of clarity and potential for misreading situations
Change speed is increasing, number of components in systems increasing, cause-effect logic becoming less linear (digital transformation, service economy, internal/external trends)
1. Digital transformation
Digitization of business and technology’s role in business/operating models introduce new factors to consider:
- The changing role of technology competency in business management
- The increasing pace of competition
- Disruptive digitally native competitors
- The changing roles of IT management and IT teams in business
- The increasing significance of data quality and effective data management
- New legislation and requirements in areas such as privacy and information security
- IT management practices expanding into various business areas
- The return to or introduction of in-house software development
- New dependencies on third parties, such as providers of cloud and communication services
2. Service economy
Different impact within different organizations, most are not ready
All organizations are service organizations (service consumers and service providers)
Sourcing trends: partners, peer-to-peer (P2P), platform- or subscription-based services (PaaS, IaaS…)
Challenges:
- Multiple dependencies
- Lack of control over dependencies
- Complex sourcing models
- Lack of holistic end-to-end understanding of value streams
- Strong and volatile external factors (PESTLE)
- The expansion of service-based business models into traditionally goods-focused industries
3. Contributions of digital transformation and service economy
| Digital transformation | Service economy | |
| Volatility | Technologies are continually changing and introducing new risks and opportunities. Failing to keep pace with opportunities may result in loss of leadership; failing to recognize risks may result in loss of business | Business models and relationship models are continually changing. These changes lead to organizations repositioning in markets and industries |
| Uncertainty | The current and future states of technology and its role in business are unclear. Technology portfolio decisions are difficult to make, because new technologies emerge before older ones can prove or disprove their effectiveness | Every member of the service relationship network has limited exposure to others; an assessment of other organizations’ capabilities and the associated risks is difficult and never complete. The growing number of external dependencies increases the overall uncertainty of the organization’s current status and forecasts |
| Complexity | The number of moving parts in the technology landscape is growing. The cause-and-effect relationship is unclear. Technology is increasingly self-organizing. Procedure-based approaches to IT management are no longer effective | The number of stakeholders in a service relationship is growing, and their interdependencies are changing and never fully known. Relationships based solely on formal agreements are ineffective in mid- and long-term perspectives |
| Ambiguity | It is hard to assess the impacts of a technology event or proposal; even known effects can be contradictory and ambiguous. Few consequences can be forecasted with acceptable levels of assurance | Due to the complexity of stakeholders’ interests and the variability of social norms, it is hard to assess the impacts of a portfolio, relationship, or marketing decision. Only a few consequences can be forecasted with acceptable levels of assurance |
4. Viability of digital organizations and guiding principles
To act in a VUCA environment, consider the following recommendations and guiding principles to map VUCA challenges (consider all in every challenge):
| Characteristic | Recommendation | Focus on value | Start where you are | Progress iteratively with feedback | Collaborate and promote visibility | Think and work holistically | Keep it simple and practical | Optimize and automate |
| Volatility | Prepare for variations by investing in extra resources | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Uncertainty | Improve knowledge management and quality of information | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Complexity | Restructure for self-organization and agility | X | X | X | X | |||
| Ambiguity | Experiment to explore available options | X | X | X | X |
5. Succeeding in digital transformation From HVIT, five behavior patterns:
|
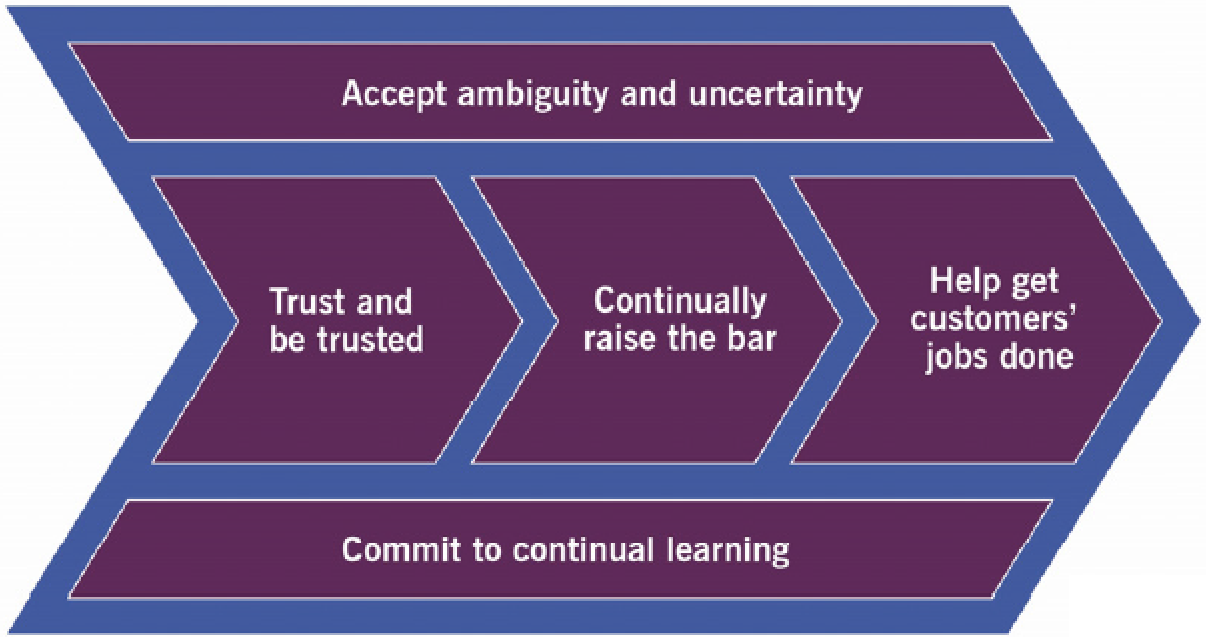 |
- Commit to continual learning: underpins all others; having right information combats uncertainty and ambiguity
6. Characteristics for a VUCA environment
7. Strategic methods to address VUCA
Create awareness, embrace it, develop appropriate behaviors
7.1 Addressing volatility
Plan for budget cuts, funding projects, programs, knowledge-sharing, communication, succession planning, decision-making
7.2 Addressing uncertainty
Organization’s absorptive capacity ability to recognize the value of new information, embed it into an existing knowledge system, and apply it to achieve the business outcomes
Must continually develop the organization’s absorptive capacity (knowledge management system)
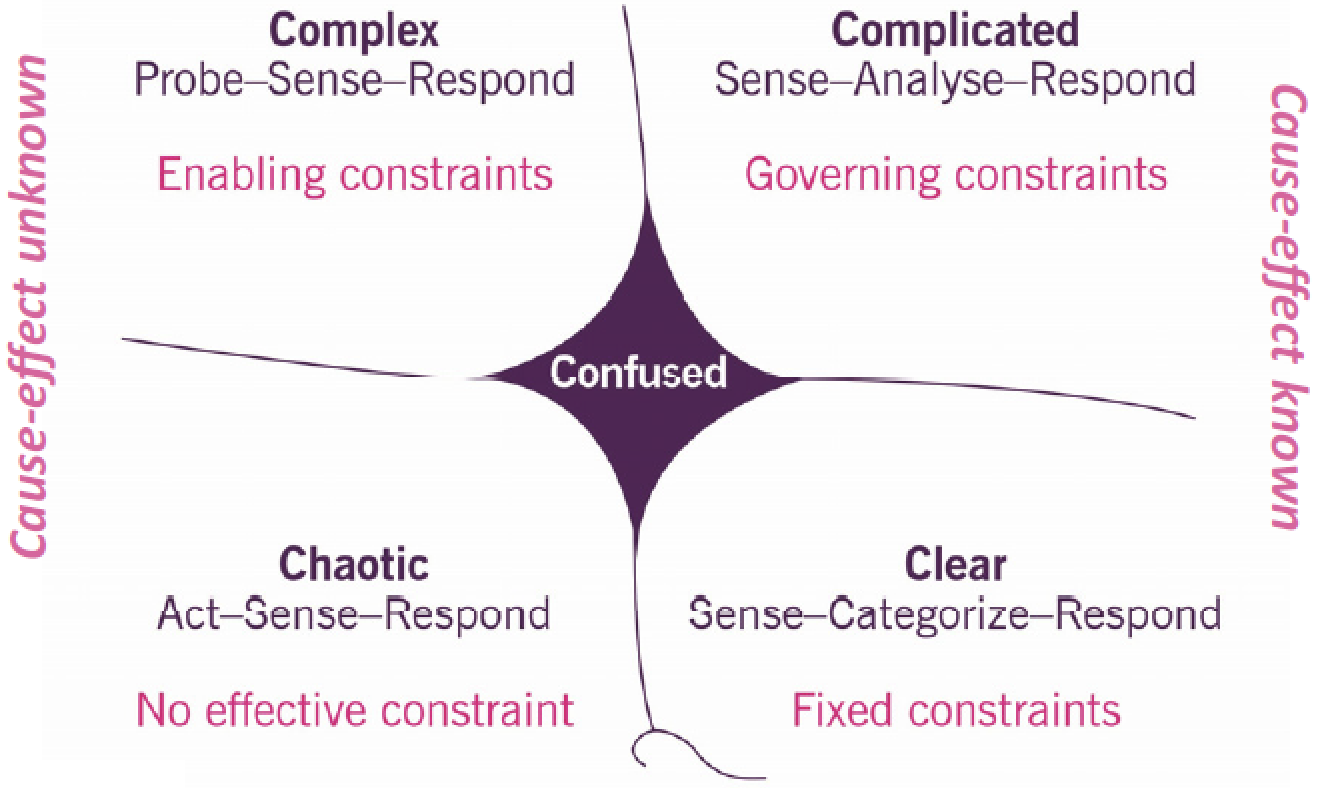
7.3 Address complexity Cynefin assesses complexity and determines appropriate actions Five domains organized by cause-effect:
|
 |
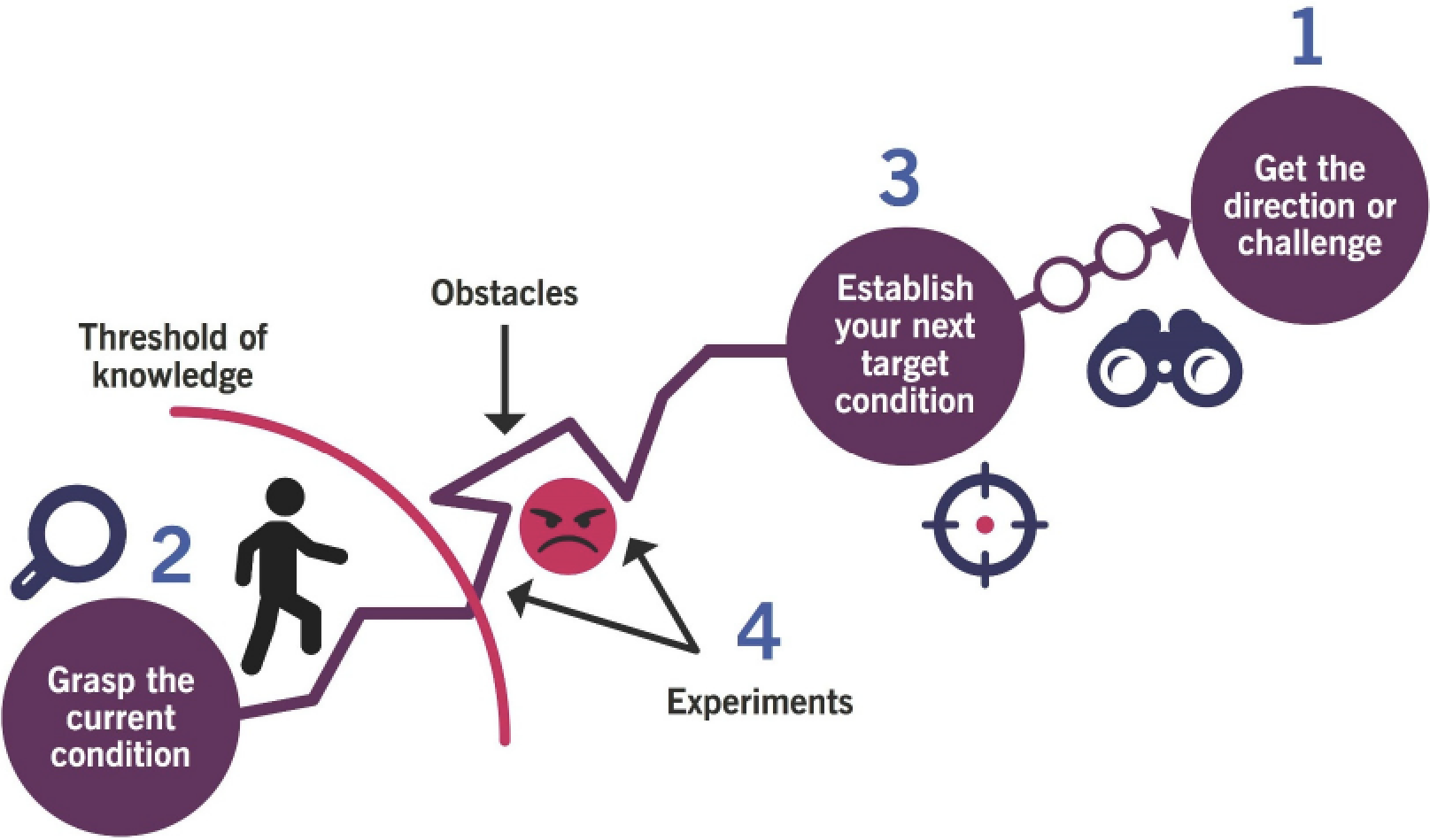
7.4 Addressing ambiguity Many options are typically available and difficult to choose the best Use experimentation and promote across organization within a safety culture Toyota Kata (mental model for scientific thinking):
|
 |
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Disruption to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
Interesting Management
-

Part 1: A good manager, better team motivation, better team productivity, better team results
When you are managing a team, “how to be a good manager” is the “must”...
-
Report optimization, increase your time management
As manager, I am doing many reports, even when I was an ITIL consultant, I still needed to do many reports...
-

Tools to get your ITIL intermediate certifications, the missing 15 points for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional
ITIL V3 is going to be obsolete...
-

The importance of the first customer meeting for the service
Managing an IT service when I start a new company is not an easy task, particularly true, if the service...



