ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) - Continual Value Co-creation
1. How users request services
1.1 Ongoing service interactions
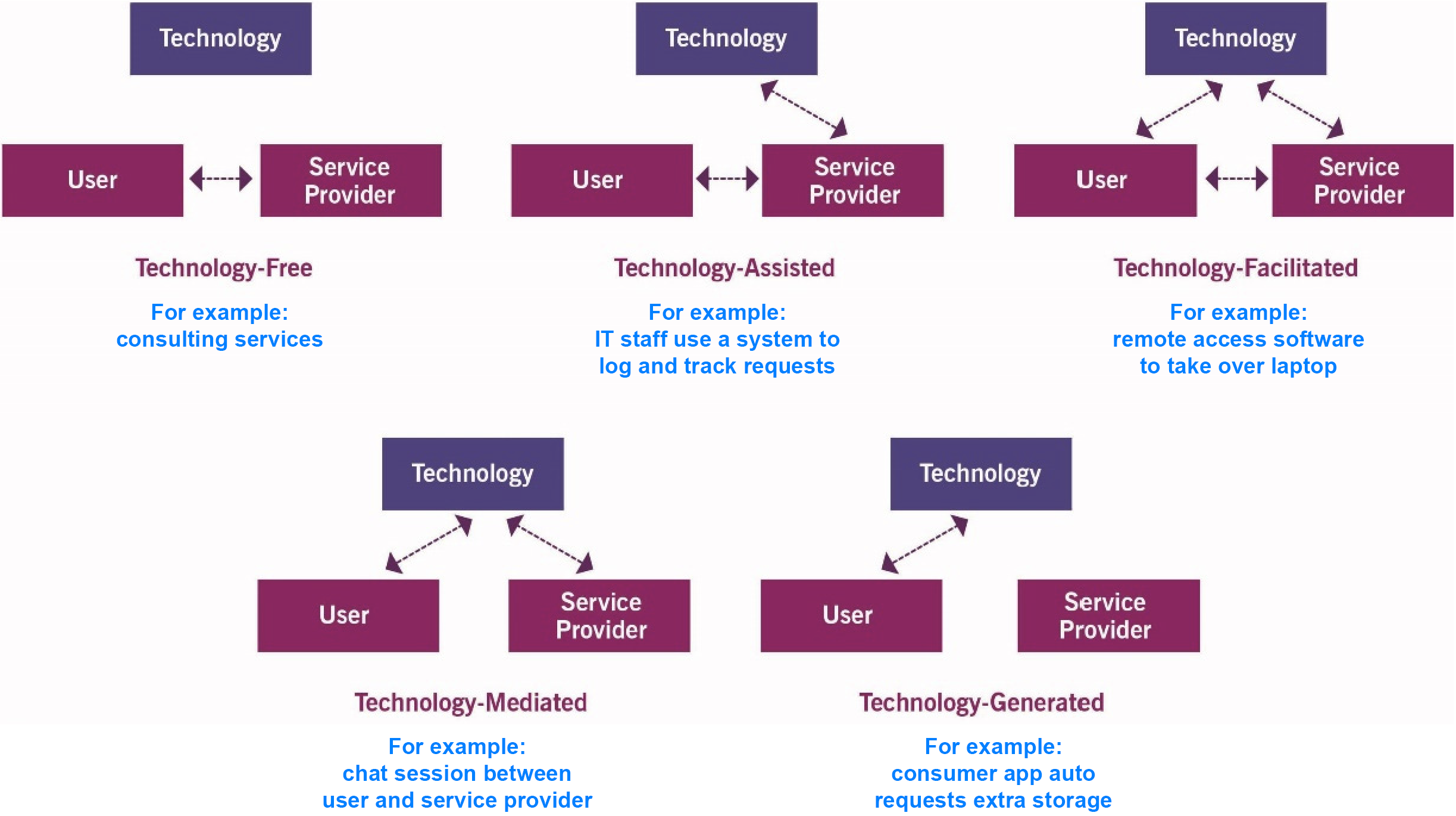
Different approaches to provision services for users:
- Push or pull ?
- Provider pushes to the user (regular reports, client s/w updates…)
- User pulls from the provider (new laptop, software product install)
- Tailored or out-of-the-box (standard for all users, or customized to preferences of individuals or groups)
- Direct or indirect (service provider employees and resources or via agents, for example an airline may use agents for passenger check-in)
- Automated or manual
1.2 Service requests
Key message: a request (service request management) from a user or a user’s authorized representative that initiates a service action which has been agreed as a normal part of service delivery
This is a significant part of the service journey:
- Approach is defined as part of service architecture and design
- Agreed during agree step
- Implemented during onboard step
- Applied during co-create step
- Has a major impact on user journey and user experience
Rules/conditions for service requests are agreed and communicated:
- Channels and means of initiating a request
- Available request options
- Responsibilities
- Procedures
- Timeframes
- Authorizations
- Costs/prices
- Legal requirements
- Any other constraints
1.3 Service desk interactions
Service desk (service desk practice) is closely integrated to other practices and support value streams
Must have defined/dedicated interfaces so the user can connect efficiently and consistently (user‐friendly, simple…)
Must have agreed rules for triage and prioritization, resolution and communication (rules will depend on type of event, impact, contact channel, service…)
1.4 Moments of truth
Key message: any episode in which the client comes into contact with any aspect of the organization and gets an impression of the quality of its service. It’s the basis of setting and fulfilling client expectations and ultimately client satisfaction
Every interaction is a possible moment of truth either positive or negative:
- Make or break the service provider in how they are handled
- Can be changed from negative to positive by service provider behaviour
Turn each negative moment of truth to a positive by utilizing the right resources and capabilities, to make the right decisions and provide the right service
A key interaction or touchpoint:
- Where user forms/changes their impression
- Only some interactions are moments of truth (every interaction is a potential moment of truth, for example a service request that generates an impression of good service)
- Key touchpoint or service interaction between the service provider and a user in which the user forms or changes his or her impression of any aspect of the service experience, service organization, products, or services
1.5 Intelligent disobedience
The act of breaking the rules to do the right thing
Simple and common in everyday lives (improves our lives and are genuinely appreciated)
To manage the unexpected when rules are not sensible:
- Recognize that in‐place rules are not always appropriate to the situation
- Encourage and equip staff with the knowledge and skills to identify legitimate customer requirements and to perceive and fulfil those requirements
- Create an environment where staff feel confident to act outside the rules when circumstances dictate
- Ensure that actions are documented to improve rules and future understanding
Remember, default action is to follow the rules
2. User communities
Activities:
- Peer support
- Knowledge articles
- Discussions and improvement initiatives
Benefits:
- Decrease demand for support and move it closer to the user (shift-left)
- Provide insights and improvement opportunities
- Help communicate news and status updates
- Improve service provider image and users’ loyalty
Creation and maintenance:
- Can form naturally or be established by the service provider
- May cover multiple services from multiple service providers
- Service provider participation in user‐created groups tends to be more effective than trying to switch users to official groups (service provider may support these groups and manage their own group)
- May link to a shared knowledge base
Superusers:
- Based on ratings or status, may be assigned to provider’s practices and they would be additional support during off-peak hours, during a crisis…
- Must receive and maintain training
3. Encouraging and managing feedback Establishing continual effective feedback gathering and processing:
Service providers need open, direct, and comprehensive feedback Users and customers may be reluctant to provide feedback, often due to negative experiences in the past |


|
3.1 User feedback
| Challenges | Solutions |
People don’t believe feedback will be acted on Feedback channels are not convenient No time to provide feedback Afraid of being punished for negative feedback Assume others have provided the feedback already |
Policy to welcome all opinions Process feedback individually, manually if possible Not just automated responses Make improvement work visible Reward feedback (gamification) Actively seek feedback Ensure interfaces are convenient and secure Monitor social media and user communities Provide feedback on social media Follow the guiding principles |
3.2 Customer feedback
| Challenges | Solutions |
Customers expect users to provide feedback Customers wait to be asked for feedback Customers don’t have time to offer feedback Customers don’t listen to user opinions, just rely on metrics and reports Feedback channels are not convenient |
Policy to welcome all opinions Provide user feedback to customers Regular human‐to‐human feedback sessions Ensure interfaces are convenient and secure Follow the guiding principles Make improvement work visible |
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV) to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.
Interesting Management
-

Part 1: A good manager, better team motivation, better team productivity, better team results
When you are managing a team, “how to be a good manager” is the “must”...
-
Report optimization, increase your time management
As manager, I am doing many reports, even when I was an ITIL consultant, I still needed to do many reports...
-

Tools to get your ITIL intermediate certifications, the missing 15 points for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional
ITIL V3 is going to be obsolete...
-

The importance of the first customer meeting for the service
Managing an IT service when I start a new company is not an easy task, particularly true, if the service...



