ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Creating a Digital Strategy - Define and Communicate a Vision and Strategy
1. Crafting the vision
Purpose: reason why an organization exists (core business)
Vision: aspirational, what it would like to be in the future; objectives it aims to achieve
Organization´s business strategy includes both vision and purpose:
- Outlines how it will achieve (e.g. what initiatives...)
- Business strategy supported by functional strategies (marketing strategy, product strategy, financial strategy...)
- Digital and IT strategy must reflect purpose, vision and business strategy
Digital strategy defines future state and how the organization will solve customer needs
1.1 Scope of the vision
Defined by the team who is responsible for the area included in the scope (organizational vision: executives; IT vision, CIO, IT director...)
Strategy management practice ensures any vision or strategy is properly scoped and led with appropriate level of authority
Two rules:
- Ensure the team includes someone with appropriate authority
- Ensure the boundaries within the scope definition are accurate (don´t include areas where there is no authority)
Governance iimpact on scoping:
- Inclusion of an area in a strategy has been authorized by the governing body, or buy a person or role representing the governing body
- Person or role responsible for the budget of that area has made funding available
- Resources have been made available by their manager, without compromising the organization´s existing operation and commitments
1.2 Defining the vision
Define a vision as a group: all stakeholders who have authority over any aspect of the strategy
May be difficult... political dynamics, different opinions; may indicate underlying conflict (independent facilitator)
Purpose of the vision is to define the desired future state of the organization. Use for strategy planning and implementation of that strategy
Vision workshop best practices:
- Representative from each business area (senior member)
- Limit numbers (8-12 people): break into small groups; then have representant for each group
- Be aware of political dynamics, sensitivities
- All voices heard; each has equal voice
- Unanimous decisions, as allowed by organization culture (consensus)
- All concerns should be addressed
- Include external stakeholders only if they are responsible for some aspect of the strategy
1.3 Guidelines for crafting the vision
Be separate from the purpose
Be succinct and specific
Be unambiguous and direct
Be aspirational and inspiring
Conveys actions and concepts that embody the organization´s cre beliefs
Be consistent with behavior and values of the organization´s executives, managers, and staff
Be unique and specific to the organization
Be focused on the organization, not technology, focus on customer experience, streamline operations, transform business models
Be based on an understanding of the organization´s consumers, how emerging technologies enable problem solving (fulfill consumer needs)
Should outline intent and outcome, provides flexibility for others in the organization to innovate, discover, and develop the vision
Be time-bound, creating a sense of urgency
2. Strategy planning
Strategy is not a one-off activity:
- Strategic activities are ongoing, reacting (dictating ?) internal and external factors
- Annual review of a strategy describes a reactive organization (technology, innovation, competition changes faster)
Strategic planning is a process:
- Can be iterative
- Must balance the time/effort to review/create a strategy with the response needed to prevent missing opportunities
2.1 Strategy cycles
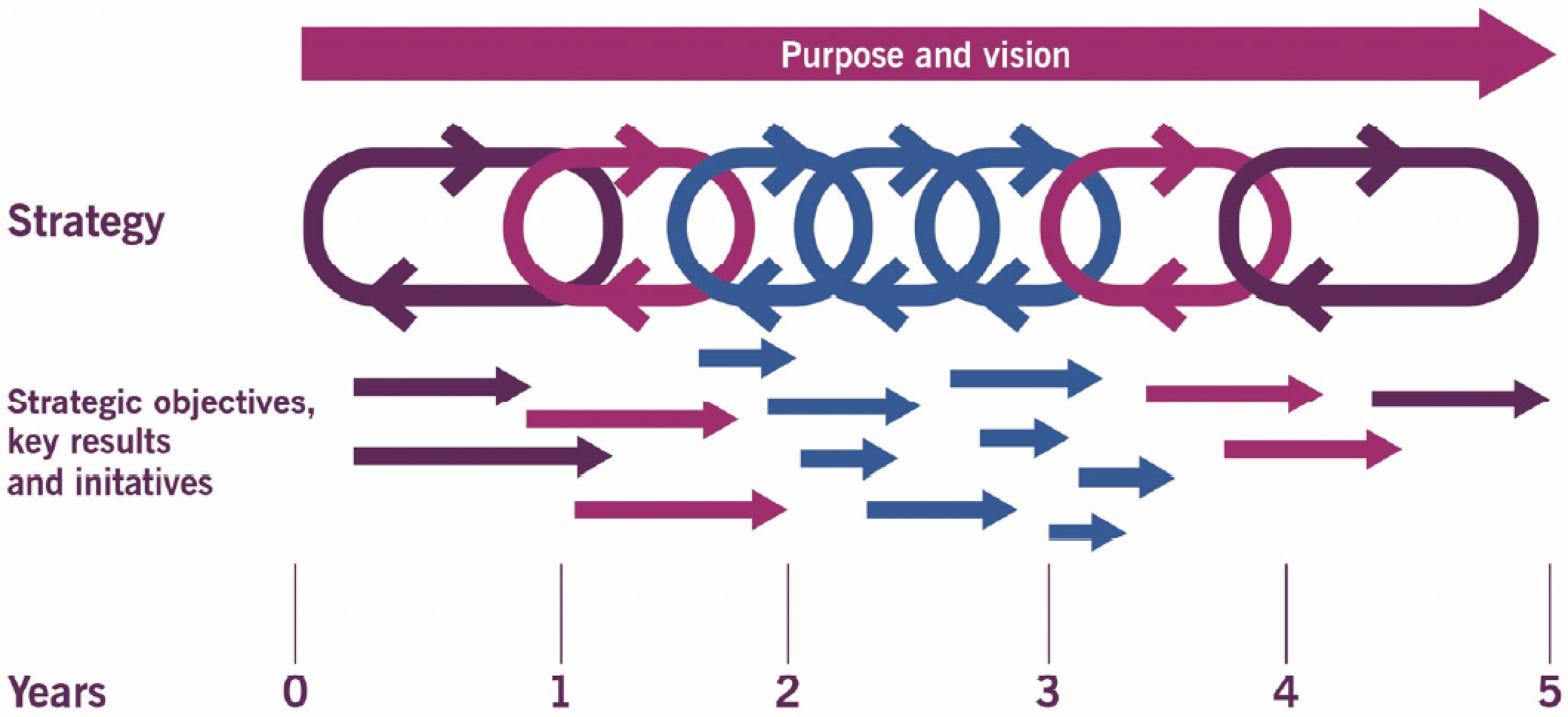
3. Strategy artefacts
A strategy is a system of artefacts; must use a structure that supports the business model, architecture, organizational structure, governance
Typical artefacts:
- Strategic assessment
- Positioning statement or analysis
- Several scenarios indicating likely outcomes if certain variables are changed
- Vision
- Business model
- Financial analyses of all options
- Plan, or several related plans
- Project and product portfolio, often together with an application portfolio
- Detailed architecture of the future-state organization, infrastructure, solution, or some other aspect of the strategy
- Risk analysis and treatment options
4. Strategy structure and content
Use collaboration tools or document management system/document sharing to manage the artefacts:
- Manage the artefacts individually rather than a single document (collection of views)
- Easier to USE; easier to update as needed (change control); protects sensitive information; parts can be delivered to who needs it rather than creating confusion
Have different versions depending on the audience, not all parts are necessary for everyone:
- Shows how the strategy can be a dynamic management tool; use a dashboard to show progress or achievements on the various elements
- Development and management different across organizations, could be a team, individual, department (cross-communication, transparency of the strategic elements). Don´t develop the strategy in isolation
5. Strategy oversight and controls
Governing body has oversight of the organizational strategy
Executives define the strategy within their area of responsibility, may create a strategy for their area of responsibility; must link all iterations
Strategic controls include:
- Measuring and reporting the progress of strategic initiatives
- Measuring and reporting whether the strategy is achieving its objectives
- Evaluating whether the strategy is still relevant in its changing environment
- Detecting unintended consequences
- Regular stakeholder meetings to consider the above, and determine whether action is required to change the strategy or any part of a related strategic initiative
- Reporting to other strategy owners whose strategy is linked to this one
- Checks against the enterprise strategy, to ensure that stakeholders do not make the organization deviate from its desired position or objectives
Go back to ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course: Creating a Digital Strategy to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification Course.
Interesting Management
-

Part 1: A good manager, better team motivation, better team productivity, better team results
When you are managing a team, “how to be a good manager” is the “must”...
-
Report optimization, increase your time management
As manager, I am doing many reports, even when I was an ITIL consultant, I still needed to do many reports...
-

Tools to get your ITIL intermediate certifications, the missing 15 points for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional
ITIL V3 is going to be obsolete...
-

The importance of the first customer meeting for the service
Managing an IT service when I start a new company is not an easy task, particularly true, if the service...



