ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Create, Deliver and Support (CDS) - Know How Practices Contribute
1. The service value stream
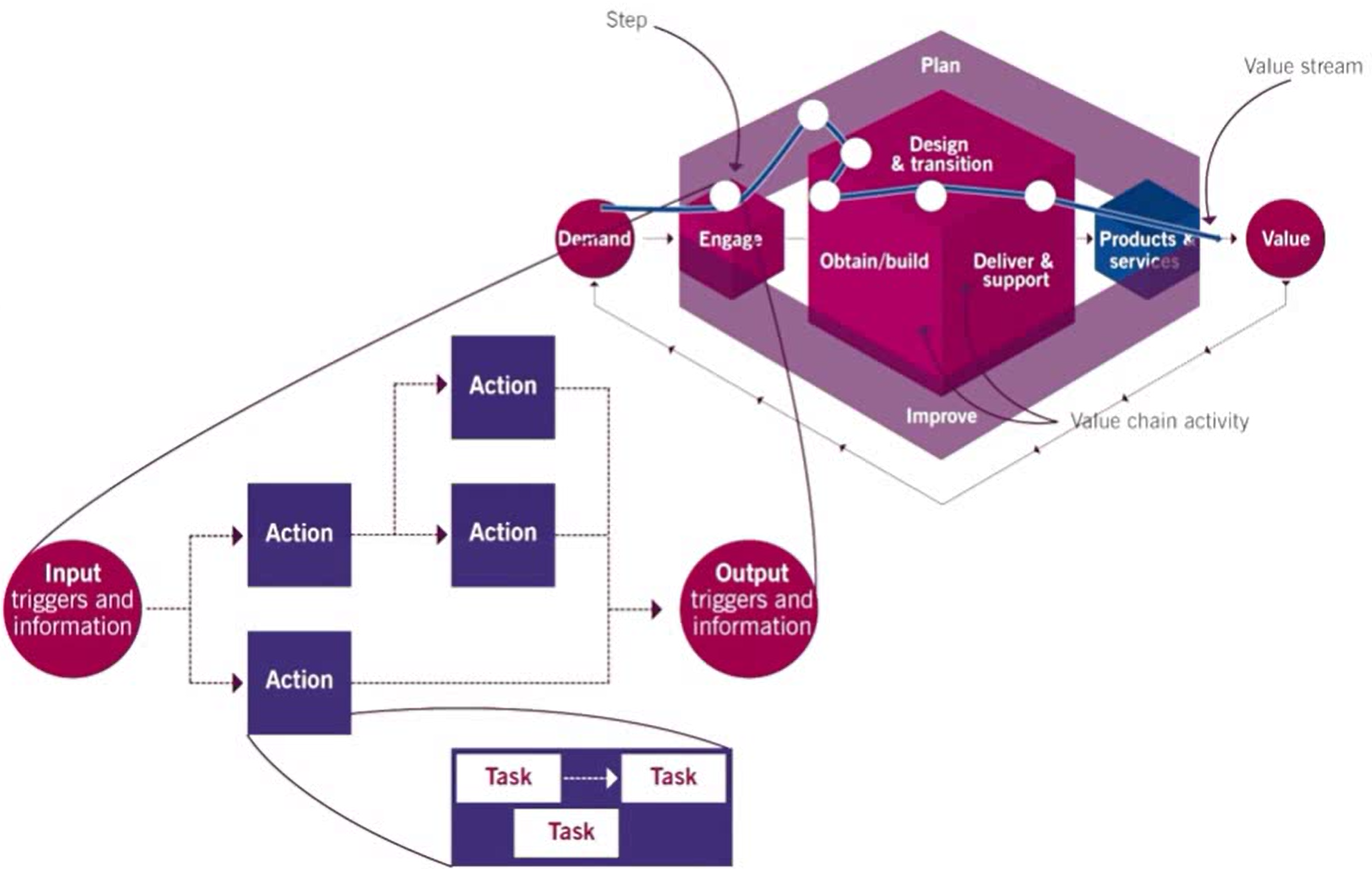
Every value stream starts with demand and ends with value. A value stream may involve many ITIL Value Chain activities:
- May be iterative
- Similar to DevOps methodologies
2. Value streams and organization
Value streams are not processes:
- Process: set of interrelated activities that transform inputs into outputs
- Value stream: the flow of activity from demand (opportunity) to customer value
Cascading value streams address the guiding principles:
- Focus on value
- Progress iteratively with feedback
- Collaborate and promote visibility
- Think and work holistically
Process tools and techniques are applicable to value streams
3. Value stream considerations
Select the right perspective
Start with demand, end with value creation
Flexibility
Granularity
Identifying steps
Step order
Map to the service value chain
Map to practices
4. Designing a service value stream
| Steps | Describing a step of the value stream |
1. Define the use case 2. Document the steps (demand to value) 3. Map the steps to the service value chain 4. If necessary, fragment to steps into actions and tasks 5. Identify the practices and associated resources needed for successful completion of each step, action, or task |
Use a standardized template:
|
5. Value stream mapping
From Lean (visualizing flow from demand/opportunity to value; planning how the flow can be improved): reduce the number of resources but still deliver the same value (no waste)
Originated in manufacturing but has great use in service management: business case writing, prioritization, optimizing service value streams, finding bottlenecks in practices, determining improvements
Build an end‐to‐end picture of how the service will be used and experienced
Involve as many stakeholders as possible
Focus on the customer and user viewpoints of every activity but include other views as well where necessary
Often done on a large wall with sticky notes and sheets of paper
Identify points of failure, areas of risk, blockage etc. (e.g. dependency on a single person, process, supplier etc.)
6. Key metrics when analyzing value streams Based on workflows:
|
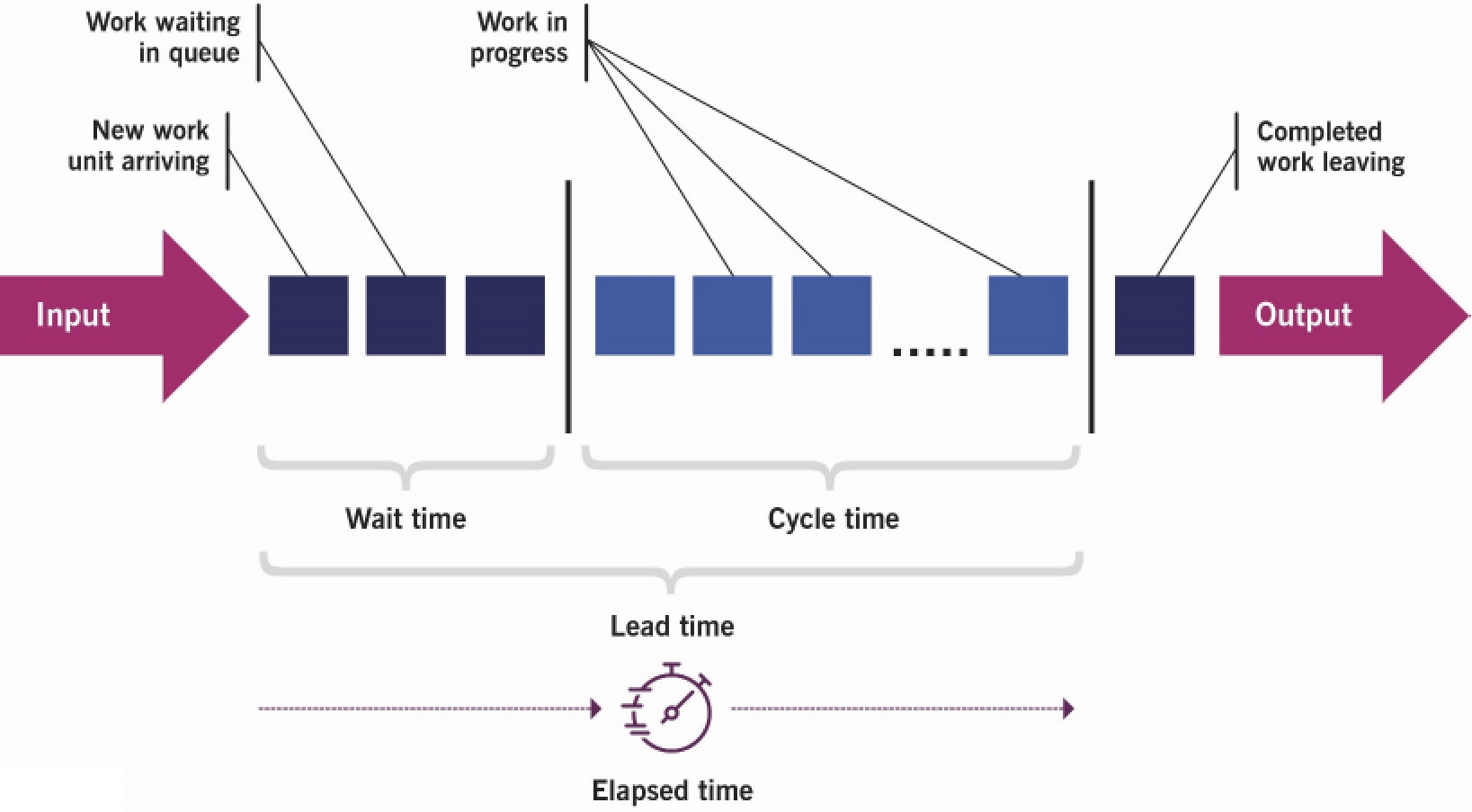 |
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Create, Deliver and Support (CDS) to finish this chapter or to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.
Interesting Management
-

Part 1: A good manager, better team motivation, better team productivity, better team results
When you are managing a team, “how to be a good manager” is the “must”...
-
Report optimization, increase your time management
As manager, I am doing many reports, even when I was an ITIL consultant, I still needed to do many reports...
-

Tools to get your ITIL intermediate certifications, the missing 15 points for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional
ITIL V3 is going to be obsolete...
-

The importance of the first customer meeting for the service
Managing an IT service when I start a new company is not an easy task, particularly true, if the service...



