ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course: Create, Deliver and Support (CDS)
To begin this course, go to the main page ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course.
2. Create, Deliver and Support (CDS)
- 2.1 Team culture and differences
- 2.2 Employee satisfaction management
- 2.3 Results based measuring and reporting
- 2.4 Know how practices contribute
- 2.5 Value stream for a new service
- 2.6 Value stream for user support
- 2.7 Know how to create, deliver and support
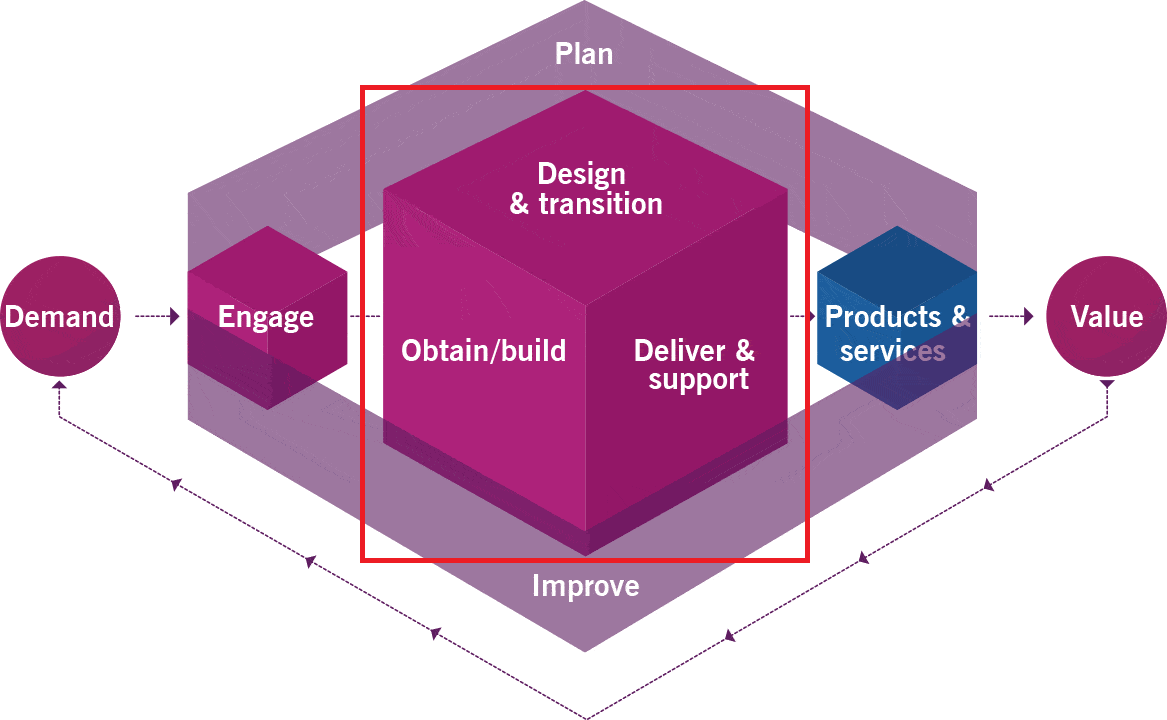
1. Types of organizational structures
| Functional | Hierarchical, formal lines of authority, determine power, roles and responsibilities Often based on functional areas like HR, IT finance, marketing etc. |
| Divisional | Based on markets, products, geography etc. Each division may have profit & loss accounting, sales, marketing, engineering, etc. |
| Matrix | Grid of relationships Pools of people who move across teams Often has dual reporting lines (e.g. functional and product) Can provide more speed and agility |
| Flat | Very little hierarchy Removes decision making barriers, enabling fast decisions Challenging to maintain as organization grows |
2. Integrated/collaborative teams Servant leadership:
If you’re thinking of moving to cross-functional servant leadership:
|


|
| Collaboration | Cooperation | Algorithmic tasks | Heuristic work |
| Work together towards a shared goal/objective | Separate goals can lead to silo working | Follows a defined process, with established instructions | Depends on human understanding and intervention |
| Shared and integrated goals | Aligned goals | Follow the rules | Learn or discover what is needed |
| Everyone succeeds or fails together | Individuals and teams succeed independently | Clear inputs, outputs, instructions, branches etc. | Needs flexibility, information, knowledge and experience |
| Goals and resources aligned in real time | Cooperative, friendly, willing to share information | Reassignment and handover between teams where needed | Collaboration, swarming and DevOps often appropriate |
| Technology is necessary but not sufficient | Technology is necessary but not sufficient | People doing the work may recognise opportunities to improve how it is done. This should be part of their role | New insights can be recorded for future use, moving some work to algorithmic (removing toil) |
| Needs respect, trust and transparency | Less need for trust and transparency | ||
| Everyone needs to understand how they contribute to the big picture | Everyone needs to understand their own role | ||
| Need to understand PESTLE factors for all stakeholders | Need to understand PESTLE factors for own role | ||
| Needs multi-channel communication (stand-ups, face-to-face, active listening, tool-mediated, etc.) | Needs effective communication |
3. Team capabilities, roles, competencies
Traditional IT roles were technically focused in areas such as programming, business analysis, technical support, designers, etc.
Newer roles require more flexibility and regular change
Many IT and ITSM roles now require business skills such as:
- Ability to manage and motivate a team
- Relationship management
- Negotiation
- Supplier and contract management
Professional ITSM competencies:
|
 |
Developing a broad set of competencies:
- Specific training ‐ business analysis, programming, ITIL etc.
- Job descriptions that include full technical and non‐technical skills
- Recognizing non‐IT experience (team management, procurement, etc.)
- Including ‘soft’ skills like communication and leadership in role descriptions
- Performance management, rewards and appraisals reflect full range of skills
- Opportunities for training and development in all areas
- Encouraging CPD (Continuing professional development)
- Role‐based models, based on job descriptions, with career paths
- Competency based models focussed on generic capabilities
- Hybrid role and competency based models combining both
Go back to ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification Course for the other chapters if you completed this Create, Deliver and Support (CDS) chapter.
Interesting Management
-

Part 1: A good manager, better team motivation, better team productivity, better team results
When you are managing a team, “how to be a good manager” is the “must”...
-
Report optimization, increase your time management
As manager, I am doing many reports, even when I was an ITIL consultant, I still needed to do many reports...
-

Tools to get your ITIL intermediate certifications, the missing 15 points for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional
ITIL V3 is going to be obsolete...
-

The importance of the first customer meeting for the service
Managing an IT service when I start a new company is not an easy task, particularly true, if the service...



